Blockchain is a new technology for verifying data transactions. It is a way of securing data by breaking it down into chains of blocks to allow many functions of centrally organized information systems to be decentralized. Blockchains can be used anywhere information needs to be securely managed and verified. Blockchain technology is based on a decentralized open-source network managed by all of the network participants and consistently, verifiably, efficiently, and unambiguously documents transactions on a continuous basis using signatures. The open source aspect and the integrated redundancies based on the number of participants in the block protect the data against manipulation and deletion.
This allows transactions, digital goods, values, processes, and tasks to be identified, validated, and exchanged. The disruptive potential is created by the secure management and verification of information and values, which allows users to circumvent the trustworthy intermediaries previously required for such tasks. The roles previously assumed mostly by financial and insurance service providers could now potentially be usurped. With peer-to-peer communication, the parties no longer have to depend on reputations of trust because the information is unambiguous and fully retroactively visible.
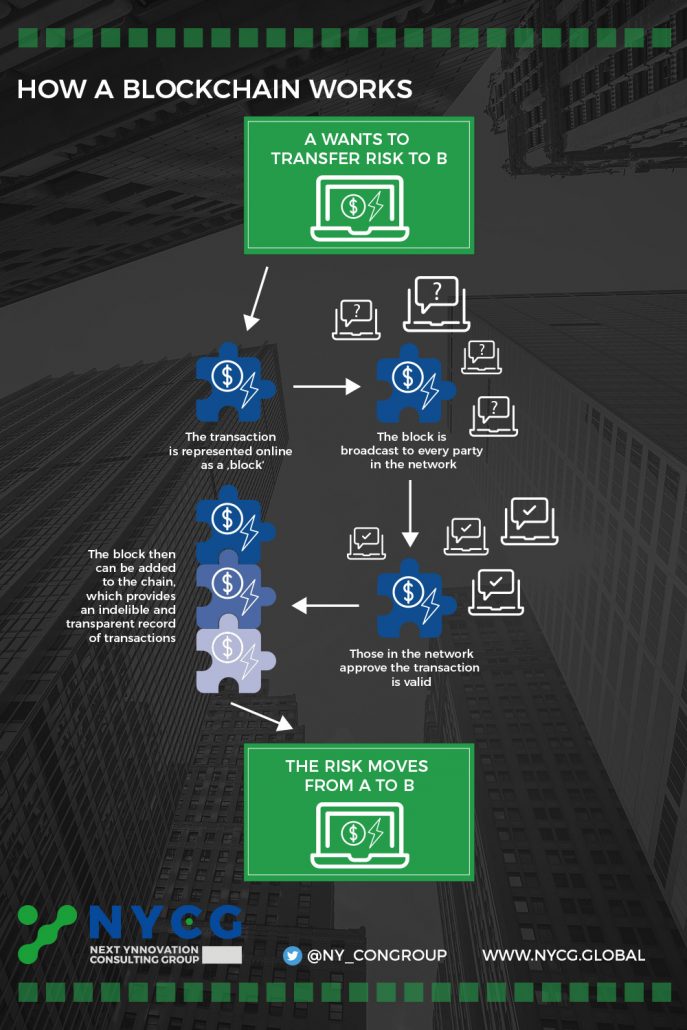
The Blockchain describes a publicly accessible ‘cash ledger’, which cannot be edited retrospectively. Data (for example, transaction data) is entered into the ‘cash ledger’ in the form of blocks.
Data is collected over a certain timeframe, added to a block and then checked for validity. Verification of validity is dependent on the type of Blockchain. It is generally distinguished between proof-of-work and proof-of-stake; other procedures are used more rarely.
Proof-of-work requires a resource-intensive computing task, which can be solved by several attempts. A fraud attempt becomes economically unattractive due to the required resources. The technical prerequisites for a fraud attempt currently do not exist; it is technically hugely difficult to impossible.
With proof-of-stake, it the respective technology concept’s stakes that are decisive, independent of the use of resources. These can be tokens of the respective Blockchain Technology such as Bitcoins – but do not have to be a cryptocurrency. As can be seen in the graphic, this can also be the transfer of risks.
After checking the validity, a checksum is created from each block and its contents. This is known as a hash and is used for unique referencing. Each block contains a reference to the hash value of the previous block. This creates a continuous dependency on the previous block and chains the blocks together. New blocks are attached to the existing Blockchain and are arranged temporally.




